I’m quite certain that all of us butter. But did you know that there are different “types” of butter? Yes, types! From European butter to Irish butter and simpler butter like clarified and cultured butter, let’s discuss some of the different types of butter in this article.
I will also discuss the key attributes of each of these types of butters and what they are best used for as well. So, go on, check it out!
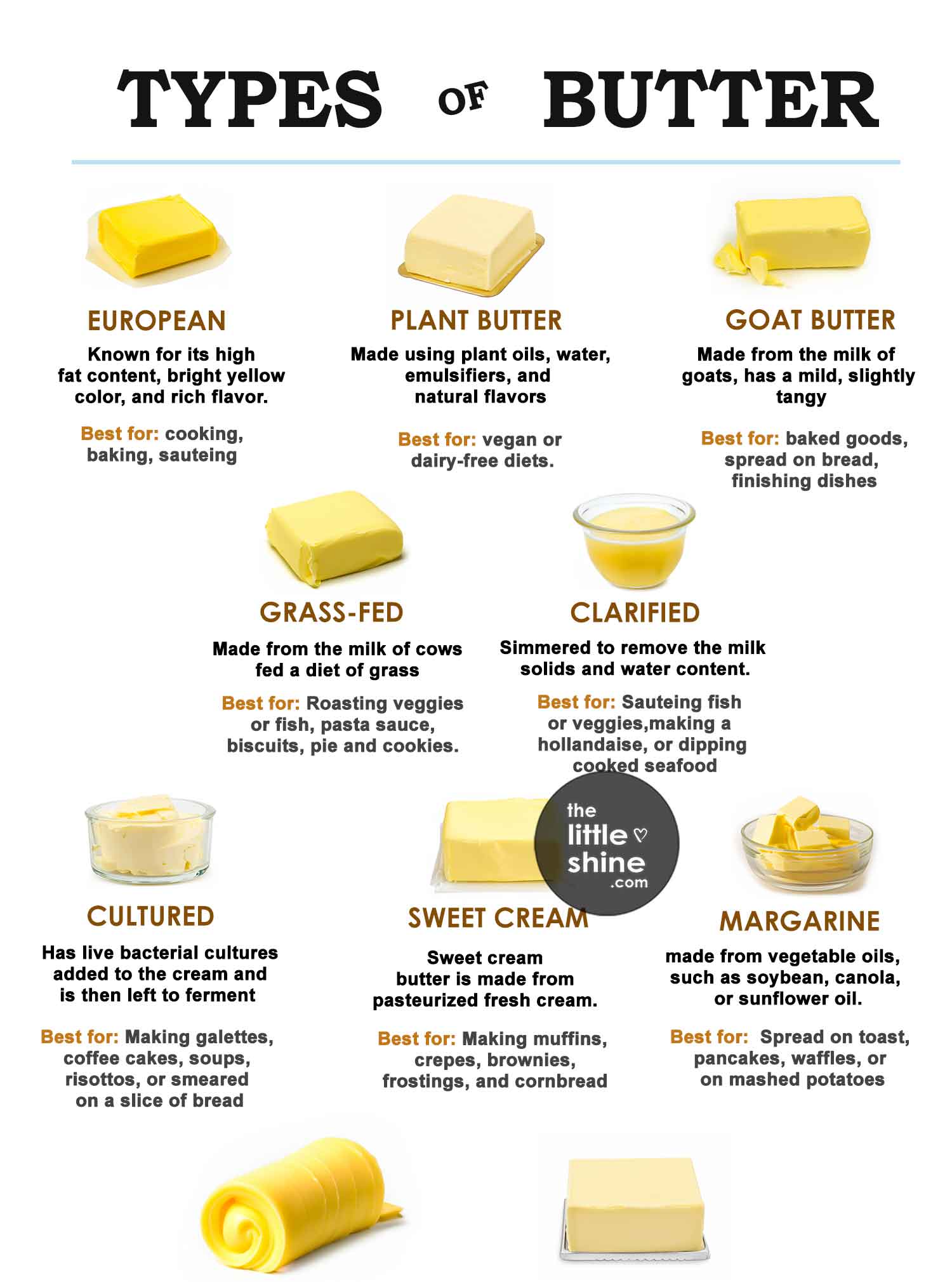
12 Types of Butter and How to Use Them
1. Salted Butter
Salted butter is that which contains salt that has been added to it. It contains at least 80 percent milk fat and incorporates about ¼ teaspoon of salt for every 4 ounces of butter.
Best used for: Use salted butter to sautée vegetables or top off savory dishes like sausage and spread on toast.
2. Unsalted Butter
Unsalted butter is butter that doesn’t contain any salt. It is often used in cooking and in also baking recipes that specifically call for unsalted butter usage.
Best used for: Cake frostings, Baking cookies, cakes, pancakes, bread pudding, and breads.
3. Brown Butter
Brown butter is a dark brown-colored butter that has a rather toasty flavor. You can gradually heat unsalted butter on the stovetop until it melts, and then the solid milk fats will start to brown, creating a fragrant and rich aroma that adds a nutty, caramel-like flavor to baked goods.
Best used for: Making cookies, brownies, granola, and pancakes. Often used in cooking for making sauces and sauté vegetables.
4. Plant-Based Butter
Plant-based butter is produced from the oils obtained from plant oils along with other ingredients like water, emulsifiers, and natural flavors. Most plant-based butter uses a combination of olive, soybean, palm kernel, sunflower, and coconut oil.
Best used for: used in vegan or dairy-free cooking or baking.
5. Grass fed Butter
Grass fed butter is made from the milk of cows fed a diet of grass and other forage. the milk from grass fed cows is richer in essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, D, E, and K, and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA).
Organic Butter Uses: Roasting vegetables or fish, pasta sauce, biscuits, pie crusts, and shortbread cookies
6. Clarified Butter
Ghee or Clarified butter is where milk solids are separated from the butter and it gives you a butter that is clear yellow. This type of butter has a high smoke point and can be heated even at high temperatures. You can quickly clarify butter at home by melting butter over low heat, then removing it from the heat once solids separate from the fat.
Best used for: Sauteing fish or vegetables, making a hollandaise, or dipping cooked seafood.
7. Sweet Cream
This butter is made from pasteurized fresh cream —rather than cultured or soured cream. You’ll find both salted and unsalted sweet cream butter. Given its name, many assume sweet cream contains added sugar, but the sweetness is natural from the fresh cream.
Best used for: It is best used in cooking, sautéing, and baking recipes. Salted sweet cream can be used to smear on biscuits or corn on the cob.
8. Amish Butter
Made by Amish family-owned and operated farms, it has a high butterfat content, ranging between 84% to 85%. Amish butter is unique because it is shaped into a cylindrical shape and is also called rolled butter. It has a high butterfat content. This butter can be used for cooking, baking recipes, and more. It is very similar to salted or unsalted butter.
Best used for: can elevate the texture and richness of baked goods like soft pretzels, pie crusts, and lavender shortbread cookies.
9. Cultured Butter
Cultured butter implements bacterial cultures into its cream base, then ferments for at least 24 hours to create a rich and slightly piquant flavor. The fermentation process is similar to the production of yogurt or sour cream. This butter has a tangy, yet subtle flavour and is high in its butterfat content.
Best used for: Making galettes, coffee cakes, soups, risottos, or smeared on a slice of bread
10. European Butter
European butter contains 82% of butterfat, it is known for its high fat content, bright yellow color, and rich flavor. European butter has a creamier, more luxurious texture that is perfect for spreading on bread or creating flaky pastries.
Best used for: Baking croissants, brioche, puff pastry, biscuits, profiteroles, pie dough, and eclairs.
11. Smen Butter
Smen butter is a fermented Moroccan butter that has been made and used in Middle Eastern and a few North African cuisines for centuries. The fermentation process brings out a strong, piquant, and cheesy flavor and aroma that is best for cooking.
Best used for: Spreading on crackers or toast, cooking or blending into coffee.
12. Goat Butter
This mildly tangy butter variation is made by churning goat’s milk rather than cow’s milk and is typically considered lactose-intolerant friendly.
Best used for: best suited for short breads, dressing vegetables, and cookies that are more tender in nature.
13. Margarine
Margarine is typically made from vegetable oils like palm and soybean oil, then mixed with water, salt and other ingredients to create its butter-like flavoring and spreadable consistency.
Best used for: Spread on toast, pancakes, waffles, vegetables, or add a dollop on mashed potatoes.
14. Compound Butter
This type of butter is known as finishing butter. The butter that has been softened to a pliable state and then has herbs, spices, or sweeteners added to it.
Best used for: Finishing cooked fish, meat, and vegetables, or making a quick pan sauce